Filtration equipment and filters consumables
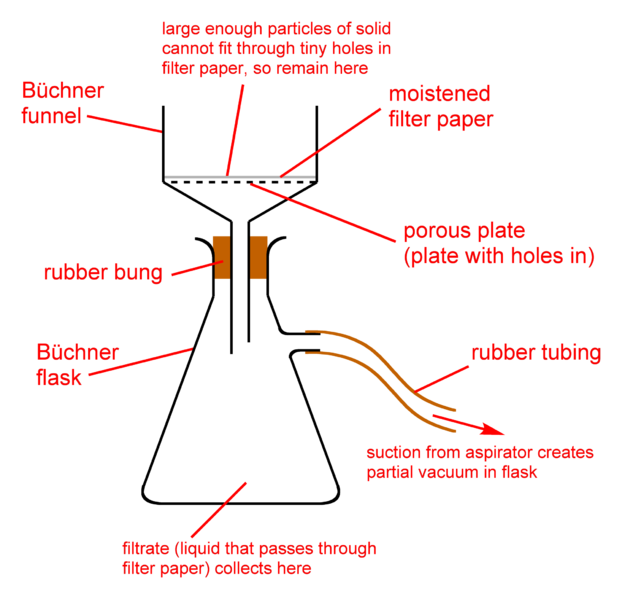
Fig. 1 Vacuum Filtration
Equipment used such as vacuum/peristaltic pump used in various filtration method where the pumps are used together with the glass apparatus and paper/membrane filter. [Request Filter Consumables Samples and appointment]
View more
When it comes to filtration, there are certain things we should always be looking out for to use the right material for our filters.
For choosing the material make for the Syringe Filters, Paper/Membrane Filters. Take a look at the process for selection for the correct filter!
Process for selecting the correct Filter
1. Determine the particle size to be retained or filtered. Membranes will retain all particles equal to, and larger than their designated pore size.
2. Assess the chemical compatibility of the membrane filter with the liquid or gas to be filtered. Consider the chemical resistance properties of all the parts that will contact the filtrate.
3. Depending on the procedure performed, the membrane color or surface pattern may be important.
4. Also consider hydrophilic or hydrophobic membranes, temperature, flow rate, throughput, and sterilization needs.
5. Determine the Diameter of your apparatus to slot your filters (Paper/Membrane Filter)
Example:Filter needed for the apparatus fitting diameter size of 13mm Particle size (0.45um) , chemical compatibility (using Acid), and the membrane needed (hydrophilic)
You will be able to find for example :PTFE Membrane filter with 0.45um pore diameter of 13mm
[Request Filter Consumables Samples and appointment]
Types of Membrane Materials
Cellulose Nitrate (CN) membrane is the most popular membrane used in analytical and laboratory filtration. CN membrane has excellent wetting properties and gives fastest flow rates with aqueous solutions.
Cellulose Acetate membrane is a mixture of cellulose triacetate and diacetate that creates a strong membrane in both lateral and longitudinal directions. In addition, the membrane has a low static charge, a very low aqueous extractability, and good solvent resistance to low molecular weight alcohols.
Mixed Cellulose Ester membrane provides a more uniform and smoother surface compared to pure nitrocellulose membrane. This membrane is typically used to count or analyze particles contained in liquids or captured from aerosols.
Nylon membrane is strong, inherently hydrophilic, and compatible with a broad range of aqueous solutions including alcohols and solvents used in HPLC work.
Polyethersulfone (PES) membrane is hydrophilic and low protein binding. No external wetting agents are required, resulting in low extractables. PES membrane generally offers fast flow rate and better chemical resistance than cellulose acetate membranes.
PTFE membrane is strong, highly porous, and inert to most chemically aggressive solvents, strong acids, and bases. Chemical and thermal limitations are imposed by the backing material.
[Request Filter Consumables Samples and appointment]
Key Filtration Terms
Bubble Point: the amount of air pressure that is required to force liquid from the largest wetted pore of the membrane.
Hydrophilic: or “water-loving”, refers to a filter’s ability to naturally absorb water.
Hydrophobic: or “water-hating”, refers to a filter’s ability to naturally repel water.
Molecular Weight Cut Off (MWCO): lowest molecular weight solute that is 90% retained by the membrane. For rapid filtration where some sample loss is acceptable, a membrane with MWCO the same as the molecular weight of the solute can be used. When loss of material of interest is undesirable, the membrane MWCO should be less than the molecular weight of the compound.
Pore Size (absolute): the point at which a particle of defined size will be retained with 100% efficiency under specified conditions.
Prewet: membranes that are inherently hydrophobic need to be specially wetted before use with aqueous filtrations. This can be done by using approximately 5 mL of chromatography-grade methanol, acetone, or compatible fluid with low viscosity (>0.6 cp)and rinsing with approximately 25 mL of water.
Throughput: refers to dirt handling capacity before membrane clogs.





